The use of a 755nm laser for vascular lesions might seem counterintuitive given the low absorption rates of oxyhemoglobin (HbO₂) at this wavelength. Cependant, the 755nm laser is indeed utilized for treating vascular conditions, and its effectiveness can be attributed to several key factors.
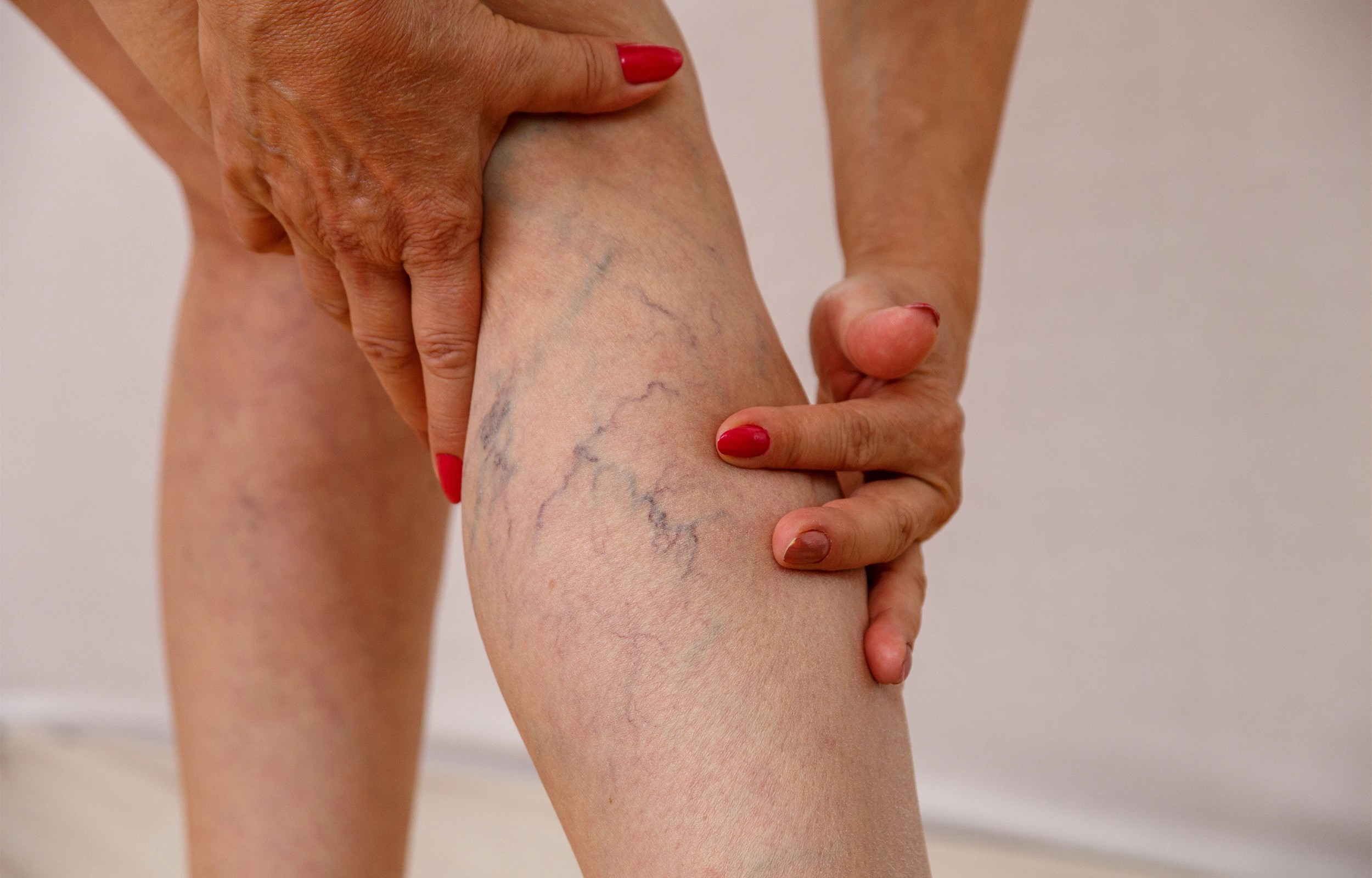
Why 755nm Laser is Effective for Vascular Lesions?
- Absorption by Deoxyhemoglobin:
- While oxyhemoglobin has low absorption at 755nm, deoxyhemoglobin, which is the form of hemoglobin that has released oxygen, absorbs this wavelength more effectively. In certain vascular lesions, such as venous dilation, the proportion of deoxyhemoglobin is higher, making the 755nm laser still effective.
- Selective Photothermal Effect:
- The principle of selective photothermal effect is fundamental in laser treatment for vascular lesions. Although the absorption peak for hemoglobin is not at 755nm (which is more effective at 542nm and 577nm), the 755nm laser can still generate sufficient heat to disrupt the vascular lesion area.
- Applicability to Superficial Vascular Lesions:
- With a shallow penetration depth of about 1-3mm, the 755nm laser is suitable for treating superficial vascular lesions like facial telangiectasias and spider veins. The heat energy from the 755nm laser is adequate to cause local vascular destruction.
- Complementary Use with Other Wavelengths:
- The 755nm laser is often used in conjunction with a 1064nm laser. The 755nm laser targets superficial vessels, while the 1064nm laser penetrates deeper, addressing larger and deeper vascular lesions.
- Role of Dynamic Cooling System:
- The Dynamic Cooling System, a technology that protects the epidermis and allows for higher energy densities, enhances the effectiveness of the 755nm laser on vascular lesions by reducing the risk of thermal injury to the skin surface.
- Limited Treatment Effectiveness:
- While the 755nm laser has some effect on vascular lesions, it is not the first choice for all conditions. Par exemple, a 532nm (green light) laser has a stronger absorption by hemoglobin and is more suitable for treating superficial vascular lesions, while a 1064nm (Sd:Laser YAG) is better for deeper vascular lesions.
What is Deoxyhemoglobin?
Deoxyhemoglobin is the form of hemoglobin that has released oxygen and is characterized by a darker color compared to the bright red oxyhemoglobin. It plays a significant role in the effectiveness of 755nm and 1064nm lasers for vascular lesions due to its higher absorption at these wavelengths compared to oxyhemoglobin.
Conclusion
Despite the low absorption of oxyhemoglobin at 755nm, the 755nm laser can effectively treat certain vascular lesions through the absorption by deoxyhemoglobin, thermal diffusion effects, and its suitability for superficial vascular issues. It is often used in combination with other wavelengths, such as 1064nm or 532nm lasers, to address a broader range of vascular lesion types and depths.
The Role of Spot Size in 1064nm and 755nm Laser Treatments for Vascular Lesions
When treating vascular lesions such as telangiectasias, the choice of laser wavelength and spot size is crucial. The 1064nm Nd:YAG laser and the 755nm Alexandrite laser are often used with different spot sizes, which is determined by the physical properties of the wavelengths and the requirements of the target tissue.
Spot Size Considerations for Vascular Lesions
- 1064nm Nd:Laser YAG:
- Recommended Small Spot Size (1.5-3millimètre):
- Reason: The 1064nm laser has a greater depth of penetration (up to 4-6mm), focusing its energy on deeper or larger blood vessels. A larger spot size would disperse the energy, reducing treatment efficiency.
- Target Tissue: Deeper or larger venous vessels, such as spider veins, which require precise heating to disrupt the vessel.
- Avantage: A small spot size provides a higher energy density, focusing on specific areas while avoiding overheating of surrounding tissue.
- Recommended Small Spot Size (1.5-3millimètre):
- 755nm Alexandrite Laser:
- Recommended Larger Spot Size (8mm or Larger):
- Reason: The 755nm laser has a shallower depth of penetration (1-3millimètre), primarily targeting superficial small capillary dilations. A larger spot size helps cover a broader area, improving treatment efficiency.
- Target Tissue: Superficial small capillary lesions, such as facial telangiectasias.
- Avantage: A large spot size allows for uniform energy distribution over a large area, suitable for treating widespread superficial lesions.
- Recommended Larger Spot Size (8mm or Larger):
Absorption Characteristics of Different Wavelengths
- 755nm Laser:
- Stronger absorption by hemoglobin but limited depth of action, making it more suitable for treating superficial lesions.
- A larger spot size can evenly distribute energy across the epidermis and upper dermis, preventing localized overheating.
- 1064nm Laser:
- Deeper penetration but weaker absorption by hemoglobin. Donc, a higher energy density and more precise spot size are needed to focus on the target tissue, such as deeper or larger venous vessels.
- A small spot size increases the energy density per unit area, enhancing the effect on deeper lesions.
Thermal Diffusion and Treatment Safety
- 1064nm Laser (Small Spot Size):
- Slow thermal diffusion with a deeper range of action, requiring a small spot size to concentrate energy and avoid damage to the epidermis and surrounding tissue.
- Particularly when treating deep venous vessels, a small spot size allows for precise focusing and prevents energy dispersion.
- 755nm Laser (Large Spot Size):
- Faster thermal diffusion, primarily affecting the superficial layer, with a large spot size that can evenly distribute heat, avoiding localized hotspots and ensuring epidermal safety.
Clinical Application Scenario Selection
| Paramètre | 1064nm Nd:Laser YAG | 755nm Alexandrite Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Taille du spot | Recommended 1.5-3mm | Recommended 8mm or Larger |
| Treatment Target | Deeper or larger venous lesions | Superficial capillary dilations |
| Applicable Area | Small area, deep vascular lesions (e.g., leg spider veins) | Large area, superficial lesions (e.g., facial telangiectasias) |
| Densité d'énergie | High energy density per unit area (small spot size enhances focus) | Relatively lower energy density per unit area (large spot size covers) |
| Depth of Action | Deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue | Epidermis and upper dermis |
Conclusion
The different spot sizes recommended for the 1064nm and 755nm lasers in treating vascular lesions are carefully designed based on wavelength, penetration depth, and target tissue characteristics. The 1064nm laser uses a small spot size (1.5-3millimètre) to focus on deep lesions, improving energy density and precision, while the 755nm laser uses a large spot size (8mm and above) to cover superficial lesions, enhancing treatment efficiency and reducing the risk of epidermal damage. This setup allows for the full utilization of the characteristics of both wavelengths, meeting the treatment needs for vascular lesions of varying depths and types.
